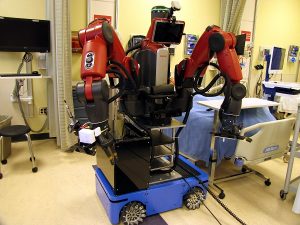
In response to the outbreak of highly infectious diseases, such as Ebola (2015) and Zika (2016), a Tele-Robotic Intelligent Nursing Assistant (TRINA) was developed to assist healthcare workers in routine patient-caring tasks, handling of contaminated materials and protective gear. This tele-nursing robot consists of a mobile manipulator robot, a human operator’s console, and software that supports various interfaces for direct teleoperation and task automation. It is also equipped with telepresence for bi-directional communication, and wireless sensors for collecting information from patient and environment. This tele-nursing robot is designed to be human-safe, versatile and usable by novice users.
At WPI, we further improve TRINA’s level of automation and user interface to reduce the cognitive and physical fatigue in the teleoperation for general-purpose assistive tasks. Beyond hospital and in-home care, we aim to endow the TRINA with general-purpose motor skills to assist tasks in warehouse, social service, and manufacturing. Our research enhances the synergy of human and shared-autonomous robots, and develop best practices for worker skill assessment and training.
Research Projects
TRINA was originally developed in 2015 at Duke University, with Prof. Kris Hauser (see the prior efforts on system integration and bi-directional telepresence user study). At WPI, the research projects on TRINA system include:
On-going Projects
- Supervisory control interfaces for individual and team nursing robot (Open to prospective PhD students)
- 2020/09-present, Supervisory control interfaces for nursing robot team
- 2019/09-present, Supervisory control for handling unreliable robot autonomy
- Multi-modal communication interfaces for nursing robots (Open to MS student for thesis)
- 2020/09-present, Verbal communication interface
- 2020/09-present, Motion & gaze tracking interface
- Shared autonomous perception-action coordination for teleoperation assistance (Open to prospective PhD students)
- Assisted teleoperation interface for nursing robots
- 2020/03-present, Assisted navigation interfaces for high-mobility tele-nursing robots (by PhD Zhuoyun Zhong, PhD Kene Mbanisi)
- 2020/09-present, interactive learning via haptic tele-nursing interfaces (by PhD TC Lin, Funded by NSF NRI grant)
- 2019/10-present, Efficient, ergonomic, intuitive humanoid tele-nursing interface: design evaluation and evolution (by PhD TC Lin, PhD Achyuthan Krishnan)
- 2019/03-2020/09, Shared Autonomous Interface for Reducing Physical Effort in Robot Teleoperation via Human Motion Mapping (by PhD TC Lin, MS Achyuthan Krishnan)
- 2018/09-2019/03, Assessing the physical fatigue in teleoperation via motion mapping (by PhD TC Lin, MS Achyuthan Krishnan)
- 2017/01-2018/04, Teleoperation interfaces via whole-body human motion mapping (by PhD TC Lin, MS Achyuthan Krishnan)
Completed projects
- Learning and planning in human-robot collaboration
- 2019/02-present, Learning and planning with parameterized symbol
- 2018/01-2019/01, High-level learning and planning for loco-manipulation
- 2017/09-2018/09, Predicting object transfer point for fluent human-robot handover
- Tele-Robotic Intelligent Nursing Assistant (TRINA) at Duke University
- 2015/01-2016/03, System integration and performance evaluation
- 2016/01-2016/05, Bidirectional telepresence for robot-mediated handover

